SHANNON, CLARE, IRELAND, March 1, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- This recent study highlights the neuroprotective potential of TFE3, a transcription factor that plays a pivotal role in counteracting key pathological mechanisms associated with Parkinson’s disease (PD). The findings reveal that TFE3 activation facilitates the clearance of toxic alpha-synuclein aggregates and restores mitochondrial function, two crucial aspects of PD progression.
As a leading neurodegenerative disorder, Parkinson’s disease is characterized by the gradual degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the brain, leading to motor impairment. Central to this degeneration is the accumulation of alpha-synuclein, a protein that forms toxic aggregates contributing to neuronal dysfunction. Simultaneously, mitochondrial impairment exacerbates oxidative stress and energy deficits, accelerating neurodegeneration.
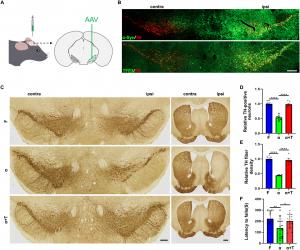
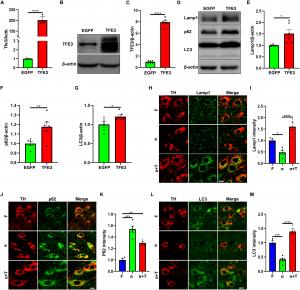
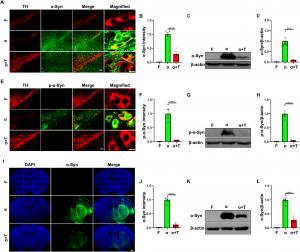
The study demonstrates that increasing TFE3 expression effectively enhances autophagy, the process by which cells remove misfolded proteins and damaged organelles. Through this mechanism, TFE3 promotes the breakdown of harmful alpha-synuclein aggregates, reducing their neurotoxic effects. Furthermore, TFE3 activation restores the function of Parkin, a protein essential for mitophagy, the selective removal of dysfunctional mitochondria. By doing so, TFE3 not only prevents the accumulation of damaged mitochondria but also fosters mitochondrial biogenesis by upregulating PGC1-alpha and TFAM, critical regulators of energy metabolism and cellular health.
This dual action—targeting both protein aggregation and mitochondrial dysfunction—positions TFE3 as a promising therapeutic candidate for Parkinson’s disease. By bolstering the brain’s natural defense mechanisms, TFE3 may help slow or even halt the progression of PD, offering hope for innovative treatment strategies.
These findings open new doors for future research into TFE3-based therapies, paving the way for targeted interventions aimed at preserving neuronal integrity and improving patient outcomes. As the search for effective treatments for Parkinson’s disease continues, the potential of TFE3 activation offers a compelling avenue for exploration in neurodegenerative medicine.
Funding Information:
National Natural Science Foundation of China 32371030
National Natural Science Foundation of China 82071395
CQMU Program for Youth Innovation in Future Medicine (Chongqing, China) W0044
Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China CSTB2022NSCQ-BHX0022
Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China CSTB2024NSCQ-LZX0008
# # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3
Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases ).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases )
# # # # # #
Reference
Xin He, Mulan Chen, Yepeng Fan, Bin Wu, Zhifang Dong,TFE3-mediated neuroprotection: Clearance of aggregated α-synuclein and accumulated mitochondria in the AAV-α-synuclein model of Parkinson's disease, Genes & Diseases, Volume 12, Issue 2, 2025, 101429, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101429
Genes & Diseases Editorial Office
Genes & Diseases
+ +86 23 6571 4691
editor@genesndiseases.com
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.