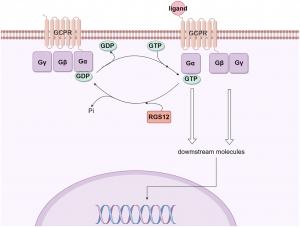
Regulation of GPCR signaling by RGS12. The Gβγ heterodimer serves to couple Gα to the receptor and to inhibit its spontaneous release of GDP.
SHANNON, CLARE, IRELAND, March 1, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- A growing body of knowledge highlights the significance of Regulator of G Protein Signaling 12 (RGS12) in maintaining cellular function and tissue integrity. As a key member of the RGS protein family, this multifunctional regulator plays a pivotal role in various physiological and pathological processes, influencing conditions ranging from cancer and osteoporosis to neurological disorders and periodontitis.
The RGS12 protein is widely expressed across different tissues and organs, where it fine-tunes signaling pathways to maintain homeostasis and respond to environmental changes. Its diverse structure allows it to interact with multiple molecular targets, regulating cellular signaling cascades crucial for tissue repair and disease progression.
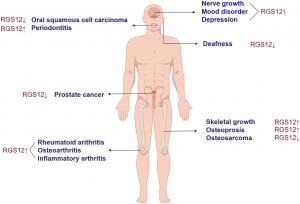
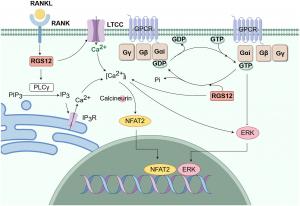
Emerging evidence suggests that RGS12 contributes to the regulation of bone metabolism, affecting the balance between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Increased activity of this protein is linked to osteoporosis, a condition characterized by bone loss and fragility fractures. In contrast, its role in fracture healing highlights its potential for therapeutic interventions targeting bone regeneration.
In the field of neurological health, RGS12 has been implicated in mood disorders, including depression and anxiety. Its interaction with key neurotransmitter pathways and oxidative stress responses suggests a link between RGS12 dysregulation and mental health disorders. Studies indicate that its modulation may present opportunities for novel therapeutic strategies to address central nervous system disorders.
Additionally, RGS12 has a profound impact on inflammatory conditions, particularly in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis. It promotes immune system regulation, influencing the activity of macrophages and the production of inflammatory cytokines. In chronic periodontitis, for example, RGS12 has been found to drive immune responses that contribute to alveolar bone loss, positioning it as a potential target for innovative dental therapies.
The role of RGS12 in cancer biology is equally compelling. It has been shown to influence tumor suppression, particularly in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), where it interacts with tumor-inhibiting pathways such as PTEN/AKT/mTOR. Reduced expression of RGS12 in certain cancers suggests its loss may contribute to tumor progression and metastasis, opening new possibilities for targeted cancer treatments.
With its diverse regulatory functions in cellular signaling, immune response, and tissue homeostasis, RGS12 stands as a promising candidate for therapeutic innovation. Its modulation could hold the key to addressing degenerative diseases, chronic inflammation, and cancer, paving the way for advancements in personalized medicine and precision therapies.
Funding Information:
# # # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3
Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases ).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases )
# # # # # #
Reference
Min Jiang, Hongmei Li, Qiong Zhang, Tongtong Xu, Le Huang, Jinghong Zhang, Huiqing Yu, Junhui Zhang, The role of RGS12 in tissue repair and human diseases, Genes & Diseases, in press, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101480
Genes & Diseases Editorial Office
Genes & Diseases
+86 23 6571 4691
editor@genesndiseases.com
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.