USA, April 24, 2024 /EINPresswire.com/ -- Researchers investigated the influence of ploidy level on mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number and gene expression in fish. They compared mtDNA copy numbers in liver and muscle of red crucian carp, common carp, and two allotriploid fish across different seasons. Interestingly, both triploid fish displayed lower muscle mtDNA copy number in winter, suggesting reduced activity and energy expenditure to maintain weight during food scarcity. Additionally, analysis of three nuclear-regulated mitochondrial genes (tfam, tfb1m, and tfb2m) revealed imbalanced allelic expression in tfam and tfb1m within the triploid fish. These findings provide valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying growth variations associated with ploidy level in fish.
Understanding the relationship between mtDNA and animal growth could provide valuable information for selective breeding in aquaculture. However, the complex interactions between genetics and environmental factors often hinders progress in this field. To that end, a recent study (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repbre.2023.12.008) published in the KeAi hournal Reproduction and Breeding investigated the cross-sectional diameter of skeletal muscle fibers in allotriploid fish with different growth traits.
The researchers selected red crucian carp, common carp and two allotriploid fish for the study. The allotriploid fish exhibit distinct growth rates and ploidy levels compared to the inbred parental species (red crucian carp and common carp). Deciphering the genetic mechanisms underlying these growth differences holds significant potential for fish breeding.
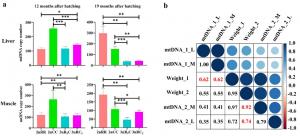
“Distant hybridization rapidly generates diverse genotypes and phenotypes, offering a rich resource for studying the role of genetic regulation in shaping phenotypes,” explains co-corresponding author Li Ren, a researcher at the State Key Laboratory of Developmental Biology of Freshwater Fish at Hunan Normal University. “Analysis of muscle fiber diameter and mtDNA copy number revealed a positive correlation between individual size and muscle fiber diameter across all fish types. Additionally, a strong correlation emerged between muscle mtDNA copy number and body weight.”
Notably, the researchers observed a decrease in muscle mtDNA copy number within the allotriploid fish during winter. “This decrease likely corresponds with reduced individual activity and energy expenditure aimed at maintaining body weight, potentially contributing to the observed growth heterosis of allotriploid fish,” adds Ren.
Furthermore, the researchers analyzed the expression levels of three nuclear-regulated mitochondrial genes (tfam, tfb1m, and tfb2m). Interestingly, they found imbalanced allelic expression of tfam and tfb1m within the allotriploid fish. Ren highlights the complex relationship between mtDNA, "The copy number and transcriptional efficiency of animal mtDNA are intimately linked not only to the characteristics of the mtDNA genome itself but also to the expression of specific nuclear genes. However, at present, a direct link between these three nuclear-encoded mitochondrial genes and mtDNA copy number variation remains elusive."
DOI
10.1016/j.repbre.2023.12.008
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repbre.2023.12.008
Funding information
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32293252, 32341057, U19A2040, and 32273111), the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2022JJ10035), the Huxiang Youth Talent Support Program (2021RC3093), the Laboratory of Lingnan Modern Agriculture Project (NT2021008), the Special Funds for Construction of Innovative Provinces in Hunan Province (2021NK1010), the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-45), and the 111 Project (D20007).
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here