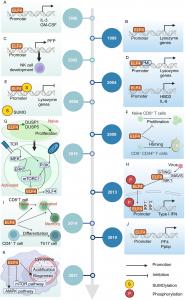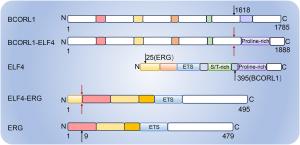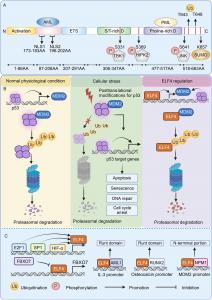
Domain structure and transcriptional regulation of ELF4. (A) ELF4 includes six functional domains: an acidic domain, an AML1 interaction domain, a conserved ETS domain, a serine/threonine-rich domain, a proline-rich domain, and two nuclear location signal
SHANNON, CLARE, IRELAND, March 10, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- ELF4, a transcription factor belonging to the ETS family, has emerged as a pivotal regulator in cell differentiation, immune system function, and cancer progression. This newly published review underscores its molecular complexity and clinical significance, shedding light on its dual role in tumor suppression and oncogenesis.
ELF4 is highly expressed in various tissues, including hematopoietic cells, placenta, and the gastrointestinal tract. Its activity is tightly controlled through post-translational modifications and intricate signaling pathways, allowing it to modulate key physiological processes. Notably, ELF4 plays a critical role in osteogenic, adipogenic, and neuronal differentiation, positioning it as a central player in tissue development and regeneration.
In the immune system, ELF4 is a crucial transcriptional regulator. It facilitates immune responses by activating cytokines such as IL-2 and GM-CSF, thereby enhancing T-cell function and innate immunity. However, ELF4 dysregulation has been implicated in immune-related disorders, including autoimmune diseases and inflammatory conditions. Its involvement in immune cell differentiation and tumor microenvironment interactions makes it a promising target for immunotherapy strategies.
In oncology, ELF4 displays a context-dependent role. It can act as a tumor suppressor by promoting DNA damage repair and regulating cell cycle checkpoints, thereby preventing uncontrolled proliferation. Conversely, in certain malignancies, such as leukemia, colorectal cancer, and glioblastoma, ELF4 is overexpressed, contributing to cancer stemness, metastasis, and therapy resistance. This paradoxical role highlights the need for a deeper understanding of tumor heterogeneity and ELF4-mediated gene regulation.
The review emphasizes ELF4’s potential as a biomarker for cancer prognosis, with its expression levels correlating with tumor stage, immune infiltration, and patient survival rates. Additionally, its interaction with signaling pathways such as PI3K, MAPK, and p53 suggests that targeting ELF4 may open new avenues for precision medicine and targeted therapies.
Despite significant advancements, many aspects of ELF4 function remain unresolved. Further research is required to decode its regulatory mechanisms and develop therapeutic interventions that harness its unique properties.
Funding Information:
National Natural Science Foundation of China U23A20451
National Natural Science Foundation of China 82273310
National Natural Science Foundation of China 82372917
National Natural Science Foundation of China 82173313
Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, China 2022CFA016
Basic Research Support Program of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (China) 2023BR038
# # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3
Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases ).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases )
# # # # # #
Reference
Dian Hu, Zerui Zhang, Yijun Wang, Siwen Li, Jiaqian Zhang, Zhangfan Wu, Mengyu Sun, Junqing Jiang, Danfei Liu, Xiaoyu Ji, Shuai Wang, Yufei Wang, Xiangyuan Luo, Wenjie Huang, Limin Xia, Transcription factor ELF4 in physiology and diseases: Molecular roles and clinical implications, Genes & Diseases, Volume 12, Issue 3, 2025, 101394, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101394
Genes & Diseases Editorial Office
Genes & Diseases
+ +86 23 6571 4691
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.